Introduction
The world is like a chessboard, where every square represents a country. These squares are a symbol of a unique population, culture, history, resources, and a system of governance. The game combines the economies, follows multiculturalism, and witnesses diplomacy in Geopolitics relations. For instance, The Arctic: a frozen area capped with oil and natural gas. Countries like Russia, United States, Canada, and Denmark are battling for dominance. This is a struggle to overpower, influence, and gain a strategic advantage. Here’s a catch, as the polar ice melts due to climate change, new opportunities and difficulties arise.
Hence, geopolitics is essentially a chess match nations play on a global scale which is an interplay of collaboration, power, and competition, shaped by economic interests and calculated ambitions.
Fundamentally, even if countries may appear far away, geopolitical events have an impact that eventually affects our pockets. Making wise financial decisions can be aided by our understanding of the interaction between the strengths and weaknesses based on the resources and location of each piece in the international chessboard.
Luxury living in tandem to Global scenario
In the International arena there exists large scale events, political disturbances, and various economic factors that significantly affect any deep pocket of a common man. The interplay of opulent standards, basic necessities, and global instability influences the choices and preferences of the citizens and excessively impacts the broader aspect of any country’s economy.
- Global events align with natural disasters, trade tariffs, and economic downturns that have a major impact on the preferences of an individual habitual to a particular lifestyle. This is because of the disruption in the supply chain, leading to an increase in the costs that in turn, seize the expenditure by the public
- Political unrest plummets the growth of many industries by suppressing the desire to visit a country with unstable governance. Countries with stable governments attract tourism and high-net-worth individuals
- The variables in the economic zone, prices, and policies, resort to the experiences that one comes across which, in turn, shapes both the personal lives and market structure. A weak currency limits the purchasing power while a strong domestic country can have the opposite effect
Therefore, this aforementioned thesis posits that events that occur around the world, seemingly irrelevant, have a direct or indirect impact on our financial well-being. This implies that the world economy is interrelated and that geopolitical variables are important in determining the economic circumstances that ultimately impact people’s financial circumstances.
Facets of Geopolitical tensions
Sanctions and trade wars damage international supply chains and have an impact on local and global economies. The main effects are outlined in the following points:
- Trade wars and Sanction effects
- Risk in International Real Estate Markets
- Customized Financial Plans
- Retirement Security
- Currency fluctuations
- Energy Prices and Geopolitical Instability:
- Defense Spending and its Economic Consequences
- Food Security and Agricultural Disruptions
- Shifting Economic Power: Multipolar World Dynamics
Trade wars and Sanction effects
Sanctions and trade wars damage international supply chains and have an impact on local and global economies. The main effects are outlined in the following points:
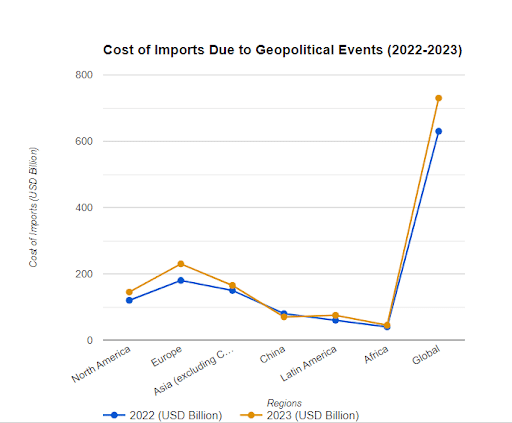
a) Increase in cost of imported items: Rising geopolitical tensions can upset global supply chains. The cost of imported items often increases as a result of this which can significantly reduce the amount of imports and negatively impact the economy. This is due to a few factors:
- Transportation costs: Shipping insurance premiums and freight prices may increase due to ship and cargo dangers brought on by instability.
- Production distortion: Political sanctions may cause major exporting countries to pause production, resulting in shortages and skyrocketed costs.
- Fluctuations in exchange rates: Economic uncertainty brought on by geopolitical conflicts may cause the value of a country’s currency to decline, raising the price of imports.
b) Tariffs in retaliation that impact exports: Imports tariffs are a form of retaliation that is used by countries against trading partners engaged in international conflicts. Due to the ascending costs associated with exports, these tariffs reduce their potential to compete in global markets. This may result in:
- Descending earnings in exports: The soaring cost of export products may cause a decline in demand that affects the overall economic expansion of a nation as foreign buyers may opt for cheaper alternatives that lower the revenue for the exporting nation
- Moonlighting: Industries that rely on exports may resort to downscaling or removal of staff if exports fall off sharply in order to cut costs. Implied by reduced profitability and bear markets, the layoffs are an anticipated outcome
- Dissection of trade: Cheaper tariffs may provide manufacturing opportunities that attract businesses, which will have a negative effect on the economy of the impacted nation.
c) Temporary benefits in domestic industries- While there may be an interim increase, the benefits are often short-lived that can cause:
- Spiraling consumer price: The cost of commodities is raised by tariffs and in order to earn profit margins, these firms raise the prices even higher. This makes the goods hefty for the buyers that were previously more affordable to import for them.
- Inefficiency: With negligible competition from International Industries, the domestic market may become complacent and this hampers the scope of innovation. A loss of incentive to innovate is costly and productivity is reduced in the global market.
- Retaliation: Nations that apply their own tariffs bore a trade conflict and damage the world economy in aggregation. This builds up tension and increases uncertainty in the home country. The effect of this is on both exporting and importing losses.
d) Damage to international commercial links over time: Repeated trade disputes and international conflicts can erode trust impacting the relationships between countries. This adversely impacts foreign and diplomatic ties across the world leading to:
- Decrease in investment: The company’s growth of making investments in nations is directly reduced or put at a halt due to uncertainty in political environments with neighboring countries, then the scenario that could have contrasted the phase if the geopolitical events never arose
- Global economic slowdown: Another factor that contributes to the phenomenon of geopolitical tensions is a fall in international trade. This slows down both the long-term and short-term gains for the nation against the potential long-term costs if pre-determined policies existed
Risk in International Real Estate Markets
The effectiveness of the regional and global environments is vital for efficient risk assessment in the global real estate market. A few things that investors analyse are the certainty of political upheaval, recession, and transformations to foreign investment regulations. In order to make well-informed investment decisions, a systematic approach to evaluate risks in the global space has to be established.
Customized Financial Plans
The financial situation and risk tolerance of each investor vary because of which financial advisors play a critical role in tailoring these plans to effectively manage geopolitical concerns. This may also demand adjustment of asset allocations or accommodating hedging strategies to safeguard against potential market volatility.
Retirement Security
The policies laid down by the government of a nation are the pivot around which the entire retirement planning moves. This policy play either enhances or undermines the stability of retirement plans. It is, therefore, essential to stay informed about policy changes and their implications on retirement planning.
Currency fluctuations
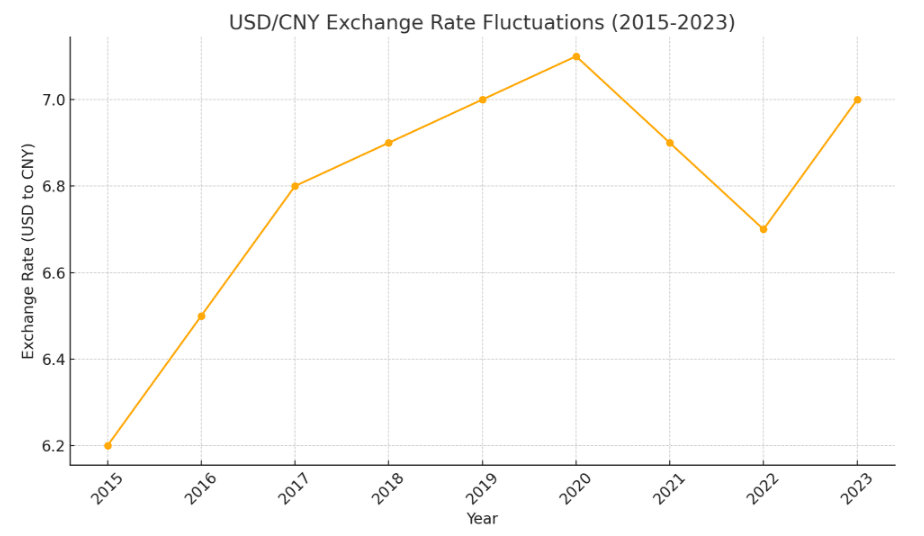
Currency fluctuations often refer to the changes in the price of one currency that occur relative to the currency of another country, primarily due to the reasons of conflicts, trade wars, and political instability. Such contingent events cause volatility in the financial market exposing the investors to the unknown risks, often ending up to become heavy losses to be borne by them. This drives them in action to move to the safe haven currencies that must have been appreciated in value as a result of this shift.
For instance, during the China-US trade war, the Chinese Yuan weakened relatively to the price of the US dollar. This strengthened the impact of inflation in China and also affected the export and import markets in both the countries. While it is meant to enhance the value of imports for China, the US is better off than before. These fluctuations, therefore, have a crucial alteration on investment and economic decisions, making currency movements vital to be considered at each stage.
Energy Prices and Geopolitical Instability
Energy-producing regions such as the Middle East and Russia have a significant impact on the global oil and gas prices. When political tensions tend to arise in these countries, energy prices eventually shoot up since the supply chain is disrupted which causes the prices to spike. High energy values often have a cascading effect on the economy, especially for the businesses that rely solely on energy supply. This leads to higher operational costs which are passed on to the consumers in terms of high prices of goods and services. The household, in turn, faces higher energy bills that reduce the disposable income and overall spending that further plummeting the economic growth.
A worldwide example of this scenario has to be that of the time of the Gulf Wars in the Middle East region when the oil prices surged. Another is Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the resulting energy sanctions by the nation, of the exports, causing a sharp rise in the energy prices.
In a nutshell, Geopolitical Instability puts inflationary pressure and causes market volatility in the energy-producing regions. As a result of this, it defines the difficulties for both the businesses and the consumers worldwide.
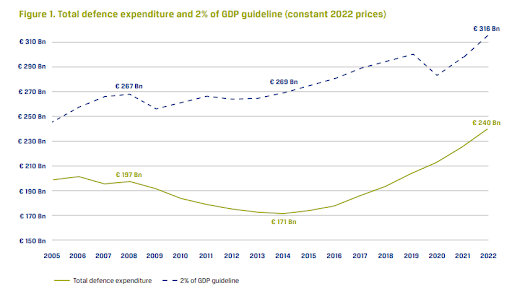
Defense Spending and its Economic Consequences
In the current world, geopolitical tension has been escalating across the globe, resulting in a huge increase in the defense sector. The power competition between the US and China has been only made other countries to increase the percentage of the budget allocated to the defense sector. For eg: North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) members have retaliated to Russia’s aggressive actions in Ukraine by increasing their defense budgets substantially. According to the SIPRI, global military spending was $2.24 trillion in 2023, which is a 3.7% increase from 2023.
However, this rise in defense spending comes at the opportunity cost of other important economic priorities. When governments allocate more funds to the military, they have to make difficult decisions regarding other important sectors as well, like infrastructure, education, healthcare, etc. This reallocation of resources can possibly result in underinvestment in such areas.
Even the United States of America, the world’s largest military spender, has been facing challenges in balancing the defense budget with other domestic needs. US is struggling with aging infrastructure, underfunded schools, and inadequate healthcare. The opportunity cost of prioritising defense over these critical areas is substantial, hindering the nation’s long-term economic development.
This increase in defense spending can lead to “crowding out”. As the governments allocate more and more resources in the military and defense sectors, it leads to higher interest rates, which leads to reduced private sector investment.
Moreover, the long-term sustainability of high defense spending is a concern for many countries. Maintaining these elevated defense budgets over a long period of time can strain the public finances and limit the government’s ability to respond to other economic challenges.
Food Security and Agricultural Disruptions
The Russia-Ukraine conflict had disrupted the grain supplies, most importantly that of wheat, which both countries exported in large quantities. Ukraine has seen its agricultural exports take a nose-dive fall due to the blockades and damaged infrastructure as a result of war, creating food shortages in regions dependent on these exports, especially the MENA region. This particular supply chain disruption has led to significant and concerning price surges in global markets.
In Africa, the food crisis has been worsened by its reliance on imported fertilizers from Russia and Ukraine. Fertilizer shortages have inflated prices more and reduced the crop yields, therefore threatening the food production across the entire continent of Africa
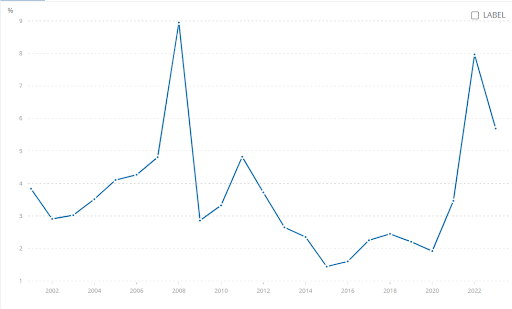
Even the global food prices rose by 23% in 2022, disproportionately affecting the low-income nations, where food consumes up to 40% of household budgets. Historically, food insecurity has been linked to political instability, and many countries dependent on Ukrainian and Russian grain imports are now facing dangerous risks of civil unrest.
Shifting Economic Power: Multipolar World Dynamics
As the Western economic dominance, especially that of the G7 diminishes, the BRICS now accounts for around 31.5% of global GDP, while the G7’s share has been reduced to 43.7%. This shift reflects not only the growing economic power of these nations but also on their ability to influence the global trade policies and alliances.
Mainly the BRICS is influencing the global economy through new initiatives like the NDB (New Development Bank), aiming to reduce the dependence on Western financial institutions like the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank. The NDB funds the infrastructure and sustainable development projects across all the member states, asserting financial independence. Recently, the BRICS have made moves to abandon the US dollar in favor of the local currencies (moving towards De-Dollarisation) for trade settlements, taking a step towards forming a multipolar economic world order.
This shift also signals towards some broader geopolitical changes. BRICS (Brazil Russia India China South Africa), despite the well-known internal differences, are trying to push back against the Western-dominated economic order. With the ongoing Russian-Ukraine conflict accelerating these dynamics, and BRICS siding with Russia or maintaining neutral positions reflects upon their opposition to the United States-led sanctions.
References
- SIPRI yearbook 2024 (2024) SIPRI. Available at: https://www.sipri.org/yearbook/2024 (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- Imf (2023) IMF / IMF Fiscal Monitor Report 2023 April update, The NewsMarket. Available at: https://www.thenewsmarket.com/news/imf—imf-fiscal-monitor-report-2023-april-update/s/fef5e390-3d71-46e1-b865-71fca91b87dd (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- World Bank Group (2023) World development report 2023: Migrants, refugees, and Societies, World Bank. Available at: https://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/wdr2023 (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- Resourcing the ramp-up: NATO and the challenge of a coherent industrial response to Russia’s war in Ukraine | rand (2022) NATO. Available at: https://www.rand.org/pubs/commentary/2024/07/resourcing-the-ramp-up-nato-and-the-challenge-of-a.html (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- (2023) Council on Foreign Relations. Available at: https://www.cfr.org/ (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- In Africa, putin’s war on Ukraine drives food, fuel and finance crises (2022) United States Institute of Peace. Available at: https://www.usip.org/publications/2022/06/africa-putins-war-ukraine-drives-food-fuel-and-finance-crises (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- The Russia–ukraine war and other geopolitical risks (2022) CFA Institute Enterprising Investor. Available at: https://blogs.cfainstitute.org/investor/2022/03/18/the-russia-ukraine-war-and-other-geopolitical-risks/ (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- Global issues : Social, political, economic and environmental issues that affect us all (2023) social, political, economic and environmental issues that affect us all –. Available at: https://www.globalissues.org/ (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- Welsh, C. and Glauber, J. (2023) Food as the ‘Silent weapon’: Russia’s gains and Ukraine’s losses, CSIS. Available at: https://www.csis.org/analysis/food-silent-weapon-russias-gains-and-ukraines-losses (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- Chaudhary, A. and Singh, R. (2022) BRICS must expand to fill vacuum left by West’s decline, Policy Circle. Available at: https://www.policycircle.org/opinion/brics-must-expand-west-decline/ (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- Hossain, M.A. (2023) BRICS: Reshaping the global economic and political order, Modern Diplomacy. Available at: https://moderndiplomacy.eu/2023/04/23/brics-reshaping-the-global-economic-and-political-order/ (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- World Economic Forum. (2024) The role of geopolitics in a multipolar world. Available at: https://www.weforum.org/reports/the-role-of-geopolitics-in-a-multipolar-world (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- GITS Blog. (2024) The impact of global geopolitics on personal finance: What you need to know. Available at: https://www.gits-blog.com/the-impact-of-global-geopolitics-on-personal-finance (Accessed: 08 September 2024).
- Economics Observatory. (2024) How are geopolitical risks affecting the world economy? Available at: https://www.economicsobservatory.com/how-are-geopolitical-risks-affecting-the-world-economy (Accessed: 08 September 2024).