Remember the time when people, our grandparents, parents or even us at some point of time used to collect and save our money in saving jars? Children would collect pennies from all around the house and shove them in those clay made piggy banks, only breaking them when in dire need of money. In fact these jars and piggy banks were not the only places of saving money, people used to hide money in all kinds of absurd places such as the walls, under their beds and what not. But as time passed, our economy became so much more complex and the financial sector so much more evolved. This was about the time when these piggy banks witnessed their demise. Making and managing money went through notable changes.
The Shifting Sands of Financial Literacy
In the past, the primary focus of financial management centred around the basic principle of spending less than one earns. However, contemporary perspectives on managing finances have evolved significantly. Today, the landscape includes a myriad of elements such as financial goals, meticulous financial planning, the incorporation of mutual funds, emergency funds, and retirement and so much more.
The traditional emphasis on mere savings has given way to a broader understanding of financial instruments. Credit cards, for instance, have become a significant factor, substantially amplifying purchasing power. Investment strategies have transitioned from concentrating on tangible assets like lands and gold to encompassing a tapestry of avenues, including debentures, equity, and bank deposits to name a few. This diversification has resulted in intricate and diverse portfolios for individuals, yielding substantial revenues.
The perception of the stock market has undergone a noteworthy shift from being regarded as a form of gambling to evolving into a legitimate full-time career in trading. Risk appetite has gone up and retirement planning has emerged as a major financial goal. Overall, there has been a notable transformation in people’s attitudes towards money, reflecting the dynamic and multifaceted nature of contemporary financial practices.
Individuals have come to recognize the significant impact and potency of compounding. This understanding has prompted individuals to adopt a proactive approach to financial planning, recognizing that keeping money idle entails an opportunity cost. Instead of allowing funds to stagnate, people are motivated to explore investment avenues that align with their financial goals, thereby harnessing the compounding effect to build wealth steadily over the long term.
Tracing the Transformation of Saving Habits to Investment Portfolios
Some of the avenues towards which money has shifted from piggy banks are:
- Equity: Investing in equities involves buying shares of a company, granting partial ownership. This asset offers potential for capital appreciation as the company grows, and shareholders may receive dividends. However, it comes with the risk of market fluctuations, requiring a long-term perspective for optimal returns.
- Debenture: Debentures are debt instruments issued by corporations to raise funds. Investors who purchase debentures essentially lend money to the company and receive fixed interest payments. These investments are considered less risky compared to equities but offer lower returns. Debenture holders are creditors and have priority in repayment if the company faces financial distress.
- Derivative: Derivatives derive their value from underlying assets like stocks or commodities. Common types include options and futures contracts. While derivatives provide opportunities for hedging and speculation, they can be complex and involve a higher level of risk. Proper understanding and risk management are crucial for investors venturing into derivatives.
- Gold ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund): A Gold ETF is an investment fund that holds physical gold or gold-related assets. It provides investors with an efficient way to gain exposure to the price movements of gold without needing to own physical gold. Gold ETFs offer liquidity, diversification, and the convenience of stock-like trading on exchanges, making them a popular choice for those seeking exposure to precious metals.
- Cryptocurrencies: Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum. Cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, providing transparency and security. While they offer potential for high returns, they are also known for their volatility. Investors should approach cryptocurrency investments with caution and stay informed about market dynamics.
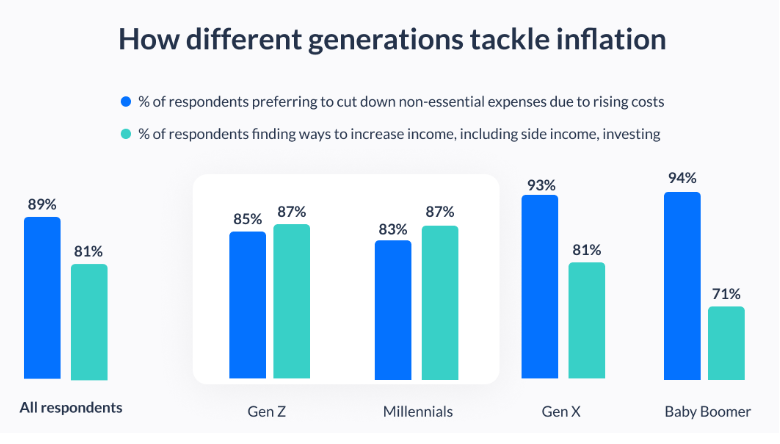
Impact of Inflation on Investment Perspectives
Inflation has prompted a realization among the younger generation that the conventional investment tools preferred by their predecessors may fall short in maintaining the real value of money. When inflation rates beat the interest rates, it leads to a deterioration in the purchasing power at the hands of people.
Consider a hypothetical scenario where the inflation rate is 3%, and a savings account offers an interest rate of 1%. In this case, the real value of the money is diminishing by 2% annually, highlighting the risk caused by solely relying on low interest instruments.
In response to this awareness, Generation Z is displaying a growing inclination towards taking up calculated risks and exploring high-interest securities. They have realized that traditional savings may not keep pace with inflation and hence seek investment avenues that offer the potential for higher returns.
The changing landscape has significantly altered Generation Z’s perception of investment ventures. Their willingness to venture into high yielding securities indicates a departure from the conservative norms of the past. This evolving approach represents that they are better equipped to combat problems like inflation.
The COVID 19 Effect on Financial Perspectives of GenZ
COVID 19 in addition to physical well being also impacted the financial being of people worldwide. Increasing unemployment and declining household income made people financially vulnerable, scarring them and hence leading to a change in the attitude of people towards income and its management.
Although the COVID pandemic has affected every generation in some kind of way, the most profound impact of this epidemic is said to be on GenZ as compared to their older counterparts. They witnessed how economic hardships can dawn without warning at a sensitive age which led to reshaping of their worldview for the rest of their lives and taught them the importance of securing their financial futures.
Here’s how it altered their financial perspectives:
- They realized the uncertainty prevailing in the job market and the importance of having multiple sources of income. This may include rental income, return on investments such as interest, dividend etc. aside from their main source of income which may be salary or profits from business.
- COVID 19 led to a heightened sense of mortality and the need to protect their loved ones financially as well as getting financial support to cover medical expenses and emergencies leading to increased importance of life and health insurance.
- They realized the importance of having multiple bank accounts for different purposes. One a basic risk free savings account to have liquid money that can support them for a few months in case of emergencies.Second a tax free retirement account that can be accessed only at the age of 65 and that grows over a period of time and thirdly an active investment account.
- It has led to educational institutions recognizing the importance of financial literacy and a curriculum on managing personal finances.
- It has led to people realizing the importance of starting early and the cost of delaying investments.
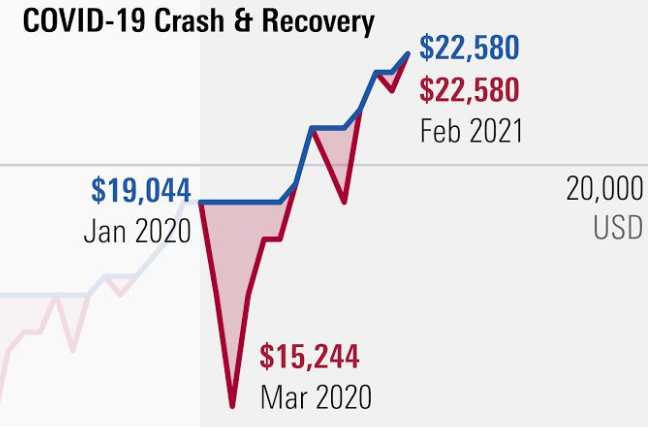
- The COVID-19 disturbance jolted the stock market, catching many off guard. Surprisingly, it created a positive shift in financial attitudes. Recognizing the importance of emergency savings became clear. Despite the initial chaos, the market rebounded within six months, instilling renewed confidence. Strategic risk-takers not only recovered losses but also seized emerging opportunities, thus redeeming the confidence of people in the stock market.
The Rise of Financial Literacy Education and Diverse Career Opportunities for GenZ
Ever since the growing recognition of the importance of financial literacy for the GenZ, educational institutions are slowly taking a step forward to help this generation not only make money but also manage it. There are various finance courses available online or even being provided as optional subjects in schools and colleges.
However, the biggest source and contributor to this knowledge are digital platforms namely LinkedIn, Instagram etc. Various creators throughout the world impart awareness, advice and knowledge on budgeting, investing avenues and other financial matters which has led to coinage of the term ‘FinTok’. Being born in the era of smartphones, internet and digital platforms like Youtube, the GenZ’s not only use these resources for the purpose of entertainment but also as a source of accessing a vast pool of information. Most of the financial knowledge and interest they possess today is through these platforms and a huge proportion of GenZ’s have their money invested in some place or the other.
Finance in the modern world is the most fast paced industry and provides an arena of career opportunities to the young generation. This spectrum ranges from the dynamic realm of corporate finance to the high-stakes arena of investment banking and also includes avenues in portfolio management for understanding risk, return and market trends.
These opportunities contribute substantially to enhancing the financial acumen of both individuals and companies.In corporate finance, they figure out the best ways for a company to use its money and make good financial choices. Investment banking involves big money moves, like when companies merge or go public. And in portfolio management, experts help people build and manage their investment portfolios, making sure they’re growing their money while staying within their comfort level for risk. All these facilities help individuals and companies a great deal in handling and taking control of their finances thus promoting greater financial discipline and stability.
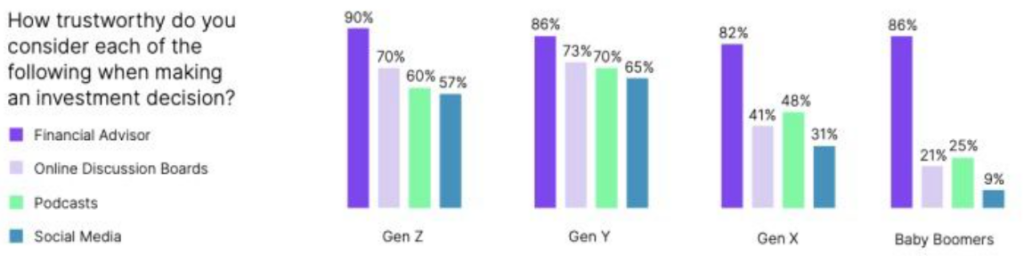
The Role of Social Media in Gen Z’s Financial Landscape
As mentioned above about the growing role of digital platforms and social media on the financial acumen of individuals, given below are the ways on how these sources influence the GenZ population:
- Peer-to-Peer Financial Influence: Social media platforms serve as a conduit for sharing financial experiences and advice among Gen Z. While this peer-to-peer exchange can foster financial awareness, it also introduces the risk of misinformation and ill-informed decisions as individuals may not be financial experts.
- FOMO and Investment Trends: The Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) is amplified on social media, influencing Gen Z to partake in investment trends without thorough research. Herd mentality, fueled by viral investment stories, can lead to impulsive financial decisions and susceptibility to market bubbles.
- Celebrity Endorsements and Influencers: Influencers and celebrities leveraging their social media presence to endorse financial products or investment strategies is becoming increasingly common these days and can sway Gen Z’s perceptions. The allure of celebrity-backed investments may overshadow due diligence, exposing individuals to potential financial frauds.
- Gamification and Social Trading Platforms: Social media-driven gamification of investments and social trading platforms can blur the lines between entertainment and serious financial decision-making. Gen Z might be enticed by the social aspect but could overlook the inherent risks associated with speculative trading.
Fraudulent Pitfalls in the Social Media-Fueled Financial Landscape
Unfortunately, progress in any field is accompanied by certain barriers. Where digital platforms on one hand have increased investment culture and financial know-how, it has given scamsters new ideas and opportunities of taking advantage of gullible youngsters. There still exists a proportion of the population who is not well equipped with the workings of the investment market and it is this section that are the main target group of these scam artists giving way to newer obstacles and problems in the financial landscape.
- Pump-and-Dump Schemes: Gen Z, influenced by social media chatter, might fall prey to pump-and-dump schemes where the value of an asset is artificially inflated through hype, only to be followed by a coordinated sell-off, leaving inexperienced investors with substantial losses.
- Phishing Scams and Social Engineering: Social media platforms are breeding grounds for phishing scams and social engineering tactics. Fraudsters may impersonate financial institutions or influencers, luring Gen Z into sharing sensitive information or making unwise financial decisions.
- False Investment Opportunities: Deceptive advertisements on social media promising quick and substantial returns can mislead Gen Z into fraudulent investment schemes. Lack of financial experience may make them susceptible to scams that promise unrealistic gains.
- Cryptocurrency Frauds: Given Gen Z’s interest in digital assets, they may encounter cryptocurrency-related frauds. Fake Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), and fraudulent exchanges can exploit their enthusiasm for innovative financial technologies.
In navigating this landscape, promoting digital literacy, critical thinking, and emphasizing the importance of due diligence is paramount. Gen Z should be encouraged to validate financial information, seek advice from reliable sources, and approach investment decisions with a discerning mindset to avoid falling victim to social media-driven financial pitfalls and frauds.
The Unseen Impact: Financial Disparities
While the significant advancement in the financial landscape has empowered many, a stark reality emerges for the economically backward sections of society. The digital divide becomes increasingly apparent as a substantial portion lacks access to these modern financial tools. In a world where wealth creation is increasingly digital, this segment finds itself excluded from participating in the evolving investment landscape. Consider a rural community where internet connectivity is scarce, and smartphones are a luxury. The residents of such areas face barriers in accessing online investment platforms, leading to a stark contrast in financial inclusion.
Limited Access to Online Financial Platforms:
The relentless shift of major banking and financial services to online platforms increases economic disparities. Those unable to navigate the digital realm not only miss out on potential investment opportunities but are also more vulnerable to the impacts of inflation. As Generation Z embraces digital investing, a growing gap emerges between the financially literate and those left behind. This exclusion can perpetuate cycles of poverty and hinder upward economic mobility.
Consider a scenario where basic banking services migrate online, leaving those without internet access struggling to manage their finances.
Economic Inequity Amplified by Technological Exclusion:
Beyond digital exclusion, the economically disadvantaged face knowledge barriers. Investing in securities, creating portfolios, or understanding the intricacies of financial markets requires a level of financial literacy that is often inaccessible to this section of society. The lack of affordable educational resources and the absence of financial advisors further compound this issue, leaving many without the tools needed to make informed financial decisions.In underserved communities, where financial education is limited, individuals may not even be aware of the benefits or risks associated with various investment schemes. This lack of awareness perpetuates financial vulnerability.
Knowledge Barriers and the Absence of Financial Guidance:
The repercussions of the digital shift in investments extend beyond exclusion from financial markets. For economically disadvantaged communities, the looming threat of inflation becomes more pronounced. As the cost of living rises, those without diversified investments bear the loss of this economic challenge. Limited access to assets that typically act as a hedge against inflation, coupled with a lack of investment knowledge, places these individuals in a precarious position. The inability to effectively navigate these financial challenges can perpetuate a cycle of poverty, increasing existing disparities in economic well-being.
Consider a low-income family heavily reliant on traditional savings. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of their savings, making it increasingly difficult to afford basic necessities. Without access to diversified investment options, these individuals find themselves disproportionately affected by the economic consequences of inflation.
Inflation’s Unequal Impact on Economically Disadvantaged Communities:
The repercussions of the digital shift in investments extend beyond exclusion from financial markets. For economically disadvantaged communities, the looming threat of inflation becomes more pronounced. As the cost of living rises, those without diversified investments bear the brunt of this economic challenge. Limited access to assets that typically act as a hedge against inflation, coupled with a lack of investment knowledge, places these individuals in a precarious position. The inability to effectively navigate these financial challenges can perpetuate a cycle of poverty, exacerbating existing disparities in economic well-being.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, piggy banks are not uncool,it has just shifted to online stocks, EFTs etc. The evolution from the physical piggy bank to online investments symbolizes not just a change in financial tools but a broader shift in financial attitudes and aspirations among Gen Z, characterized by a proactive approach to wealth-building, a pursuit of early financial independence, and diverse lifestyle choices like the FIRE ( Financial Independence, Retire Early) and DINK( Double Income, No Kids) culture. Moreover, this advancement and revolution in financial know-how should be accompanied with inclusion of all sections of the society else it can prove to do more harm than good to our economy and our society.
References :
- Gen Z Personal Finance Global management consulting. https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/email/genz/2023/08/2023-08-22a.html#:~:text=Low%20salary%20plus%20high%20debt,post%20content%20about%20personal%20finance .
- Hoffower, H. (2021) Gen zers have barely joined the workforce, and a quarter of them are already plotting to get out as soon as possible, Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.in/policy/economy/news/gen-zers-have-barely-joined-the-workforce-and-a-quarter-of-them-are-already-plotting-to-get-out-as-soon-as-possible/articleshow/88194291.cms
- Lauria, P. (no date) Generation Z: Stepping into Financial Independence, Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/generation-z-stepping-into-financial-independence-5224362 .
- Onojodofia, F. (2023) 10 ways of Saving Money in the olden days, Cowrywise Blog. https://cowrywise.com/blog/ways-of-saving-money-in-the-olden-days/#:~:text=Saving%20jars%20were%20in%20form,money%20when%20it%20is%20needed
- Paul Miller | Feb 9 (no date) Paul Miller, Indian River Financial Group, Inc. https://www.paulmilleradvisor.com/blog/brief-history-investments#:~:text=Investing%20started%20in%20the%201600s,long%2Dterm%20investment%20projects%20overseas .