Snapshot
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that relies on cryptographic techniques for secure financial transactions, control the creation of new units, and verify the transfer of assets.
The name “Cryptocurrency” is formed using ‘Cryptography’ and ‘Currency’ indicating a network of currency backed by cryptography. Bitcoin, the first decentralized cryptocurrency, is introduced by an unknown person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Till date, the pioneer of cryptocurrency remains an unsolved mystery.
The crypto revenue worldwide aims to reach $ 250 Mn by 2025. Revenue is expected to show an annual growth rate (CAGR 2023-2027) of 9.83% resulting in a projected total amount of US$324.0m by 2027.
The advanced cryptography and blockchain technology provides an impenetrable security coverage making it nearly impossible for hackers to attack, steal or shut down the network.
Cryptocurrency provides anonymity. The users remain anonymous as the transaction is based on wallet address without revealing user identity. Hence, one can surf and use the crypto network without revealing their identity.
Cryptocurrencies are one of the fastest and cheapest ways to carry out transactions as it eradicates the involvement of any middlemen. The peer to peer transaction makes it quicker without any clearance issues.
Cryptocurrencies have a global presence. Unlike centrally regulated currencies, cryptos can be used to make overseas transactions without any legal restriction or any transaction charges.
Cryptocurrency is decentralized. There is no body governing the production and flow of cryptos making it free from state interference.
Cryptocurrency provides financial inclusion and global accessibility. Any user can have access to cryptocurrency without any external restrictions to its network.
Understanding Blockchain and Proof of Work
Most cryptocurrencies work on blockchain technology. Under this, the data is stored in the form of blocks which are interconnected with each other. Every block in the chain has data about the relative block. Thus, altering a single block will alter the entire chain. This makes the blockchain secure and reliable.
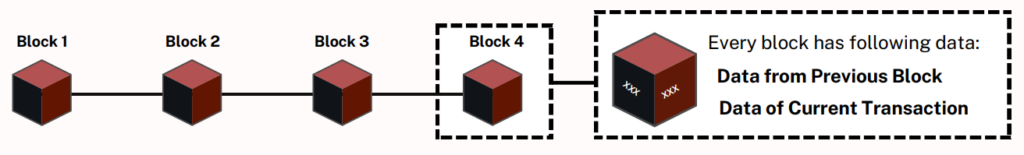
Proof of Work (PoW), a crucial mechanism in major cryptocurrencies, prevents double-spending and remains the dominant consensus algorithm. Originating with Satoshi Nakamoto, PoW’s early example, HashCash by Adam Back, aimed at spam prevention in emails, showcased its broader utility by requiring computational effort before sending emails, effectively deterring mass spamming.
Double-spending, exclusive to digital transactions, refers to the duplication of funds spent more than once, a risk absent in physical cash transactions. Unlike physical cash, digital money exists as replicable data, necessitating measures to prevent unauthorized copying and spending in different locations to maintain the integrity and stability of the currency.
Consensus Algorithm
Consensus algorithms play a pivotal role in the seamless functioning of cryptocurrencies and distributed ledgers. Serving as the backbone of these systems, they ensure that all participants reach an agreement on the state of the network, crucial for maintaining trust and reliability.

Step 1: Recording Balances:
In cryptocurrencies, your money isn’t tracked by a bank. Instead, it’s recorded in a special database called the blockchain. Every user has a copy of this database, ensuring everyone sees the same information. This prevents conflicts and keeps the system reliable.
Step 2: Keeping Coins Secure:
Public-key cryptography makes sure that users can’t spend each other’s coins. However, there still needs to be a reliable source to check if funds have been spent.
Step 3: Risk and Reward:
Validators risk losing what they put forward (their stake) if they cheat. But, there’s a reward too – they can earn the cryptocurrency of the system, made up of fees paid by users or new coins.
Step 4: Transparency:
To make sure no one cheats, the process of adding information to the database should be harder for cheaters but easy for honest users. This ensures that the validators are monitored by regular users, keeping the system transparent and secure.
Mining
Transaction Validation
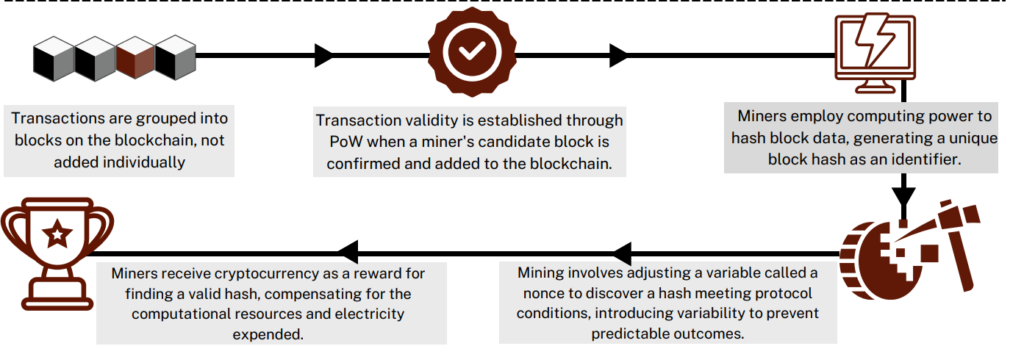
Cryptocurrency transactions necessitate updating the digital ledger, a task reserved for verified miners in Bitcoin’s distributed ledger. This system prevents manipulation and ensures security against double-spending.
Incentivizing Security
Miners earn new coins as rewards, incentivizing their active role in securing the network. With no centralized authority, mining becomes crucial for validating transactions, encouraging miners to participate in the process.
Chain of Trust
The Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus protocol, as seen in Bitcoin, ensures only verified miners validate transactions. PoW involves solving cryptographic hashes, with miners competing to crack the code and add a block to the ledger.
Increasing Difficulty and Scarcity
As miners deploy advanced machines, the difficulty of equations and competition rise. This dynamic increases the scarcity of cryptocurrency over time.
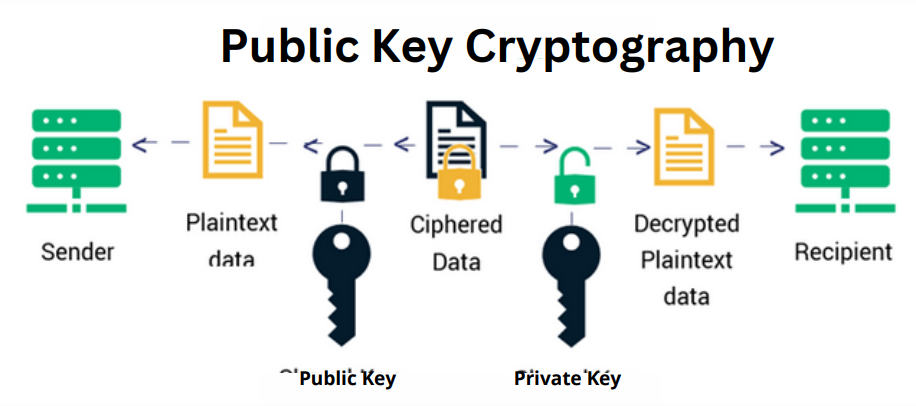
Public Key Cryptography
Public key cryptography is a method of encrypting or signing data with two different keys and making one of the keys, the public key, available for anyone to use. The other key is known as the private key. Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key. Confidentiality can be achieved using Public Key Encryption. In this the Plain text is encrypted using the receiver public key. This will ensure that no one other than the receiver’s private key can decrypt the ciphertext.
Blockchain Smart Contracts
Public Key Cryptography plays vital role in securing transactions within blockchain contracts. Smart contract execution involves the use of public and private key pairs to validate and authorize transactions, ensuring the integrity of the contract’s conditions
Secure Mail Communication
Public Key Cryptography is applied to encrypt emails, safeguarding the confidentiality of communication. Senders use the recipient’s public key for encryption, and only the recipient’s private key can decrypt and access the content, providing a secure email exchange
Cryptocurrency Wallet
In a crypto network, public and private key pairs are generated for crypto wallets. The public key creates the wallet address for sharing, while the private key is used for transaction verification and digital signatures. This ensures only wallet owner can control and move the funds Secure Mail Communication within the blockchain.
Initial Coin Offering
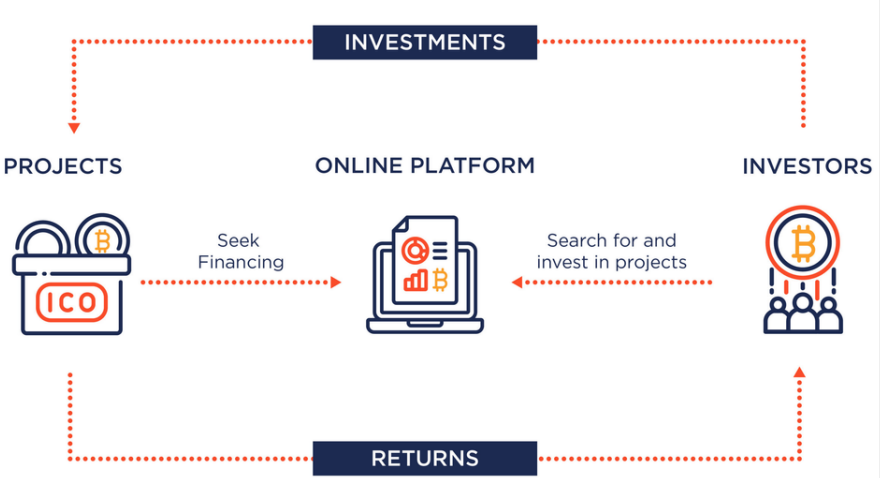
ICO stands for “initial coin offering,” and refers to a formerly popular method of fundraising capital for early-stage cryptocurrency projects. In an ICO, a blockchain-based startup mints a certain quantity of its own native digital token and offers them to early investors, normally in exchange for other cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin or ether. If the money raised in an ICO is less than the minimum amount required by the ICO’s criteria, the funds may be returned to the project’s investors. The ICO would then be deemed unsuccessful. If the funding requirements are met within the specified period, the money raised is spent in pursuit of the project’s goals.
Structuring an ICO
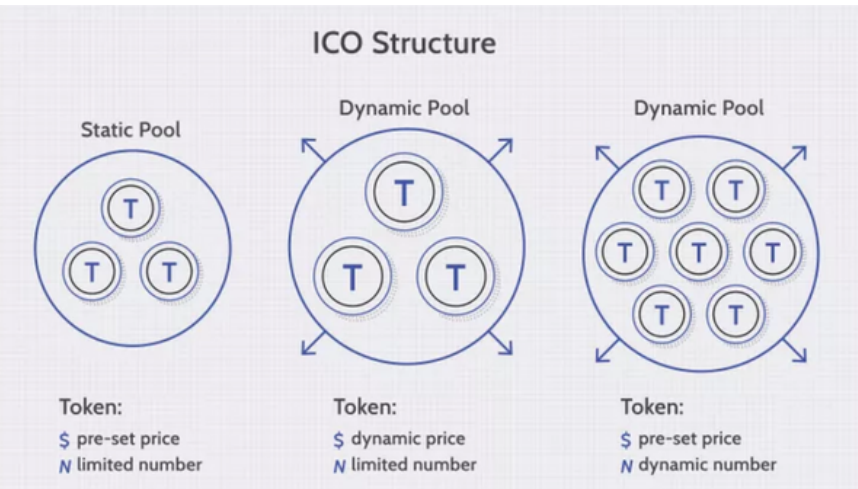
Static supply and static price: A company can set a specific funding goal or limit, which means that each token sold in the ICO has a preset price, and the total token supply is fixed.
Static supply and dynamic price: An ICO can have a static supply of tokens and a dynamic funding goal—this means that the amount of funds received in the ICO determines the overall price per token.
Dynamic supply and static price: Some ICOs have a dynamic token supply but a static price, meaning that the amount of funding received determines the supply.
Crypto-Economics
Crypto-economics is a field at the intersection of cryptography, computer science, and economics. It deals with the study and design of protocols and mechanisms that govern the behavior of participants in decentralized systems, particularly blockchain networks, aiming to achieve security, trust, and resilience without relying on a central authority. It involves creating decentralized systems that are resistant to censorship, manipulation, and unauthorized control.
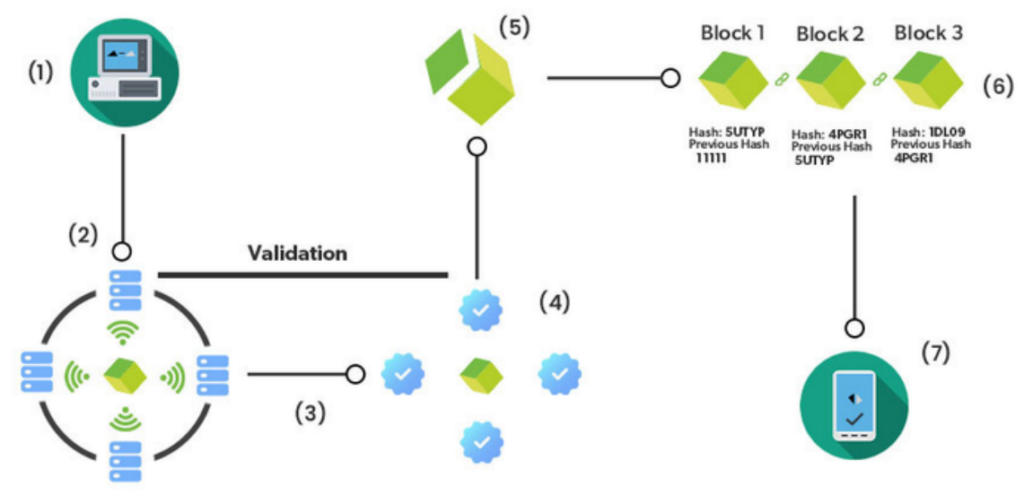
Transaction Request:
In the case of Blockchain, a transaction is requested using a device known as a wallet. A crypto economics wallet is a type of digital wallet that allows users to store and manage the cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and ether.
Transaction Broadcast:
The requested transaction is then broadcasted in a Peer to Peer network consisting of computers, which are also known as nodes. P2P networking connects a group of computers with equal data processing rights.
Transaction Validation:
After that the network of nodes validates the transaction and the user’s status, if the transaction is found to be legitimate and a success message will be delivered synchronously to the originator.
Verification Process:
Bitcoin uses digital signatures established using keypairs to authenticate transactions and senders. A verified transaction involves cryptocurrency contracts, records, etc.
Block Formation:
After the verification is done, the transaction is combined with other transactions. To create a new block of data for the ledger for keeping track of transactions.
Adding the block to the blockchain:
The new block is then added to the existing blockchain in a way that is permanent and unalterable. The ledger is spread among numerous nodes, which means that data is copied and saved in real-time on each node in the system.
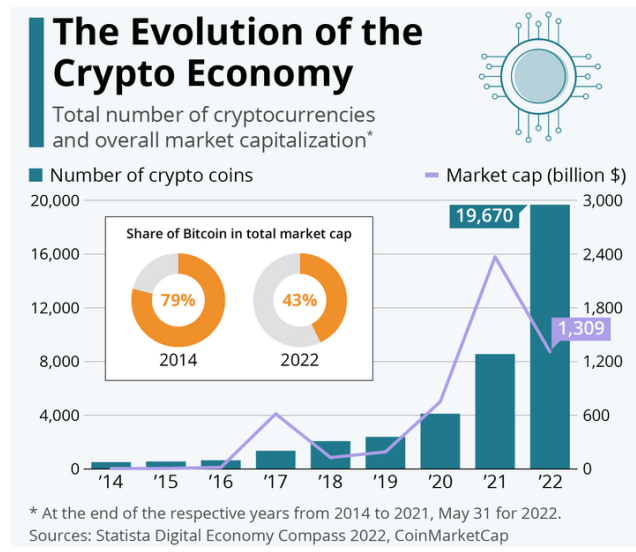
Ever since the birth of Bitcoin back in 2009, the rise of the cryptocurrency market has been marked by turbulence, with both major advances and setbacks. This infographic takes a look at the evolution of the crypto economy over the past decade, with data from Statista’s Digital Economy Compass study. Growth has gone through the roof in recent years, rising from only a few hundred virtual currencies at the end of 2014 to nearly 20,000 at the end of May 2022. This explosion, particularly seen in the past three years, can be partly attributed to the fact that creating a new cryptocurrency costs nothing and can be carried out in a few clicks.
Crypto Economics Circle
The model describes a three-sided market between miners (the supply side), users (the demand side), and investors (the capital side). These groups exchange value with each other using the network’s own scarce cryptocurrency, or token.
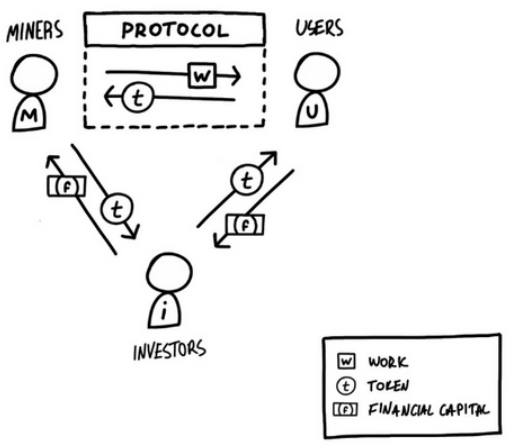
The crypto-economic circle encompasses the intricate relationship between cryptography, economics, game theory, and decentralization within blockchain ecosystems, shaping the behavior of participants and the overall dynamics of the network.
Crypto Community
A crypto community is a gathering of enthusiasts sharing a passion for cryptocurrencies, including NFTs, DeFi, and blockchain technologies. Communities, prevalent on platforms like Twitter, focus on educating members about technical concepts such as mining and Proof of Work. These communities serve as platforms for discussion, information sharing, collaboration, and engagement related to digital assets. They play a crucial role in advancing knowledge, fostering collaboration, and driving the progress of the blockchain industry. Online forums, chat rooms, and social media serve as the primary communication channels for these borderless and inclusive communities.
Knowledge Sharing: Learning from experienced community members and staying informed about industry trends.
Networking Opportunities: Build a network that can lead to collaborations, partnerships, and opportunities.
Market Insights: Stay updated on market trends, news, and potential investment opportunities.
Educational Resources: Access educational materials, tutorials, and discussions to enhance understanding.
Support and Guidance: Seek advice and support from experienced community members.
Community-driven Initiatives and projects: Engage in collaborative projects and initiatives driven by the community.
Early Access to Information: Gain early access to news, announcements, and updates from projects.
India’s Crypto Community to Swell to 156 Million Users in 2023, Leave US, UK Behind: Report by Statista The crypto community in India is set to surpass the US, UK, Russia, and Japan in terms of adoption this year. As per a recent report by Statista, India’s crypto community is expected to envelop over 156 million users by the end of 2023. The lack of a uniform and high yielding banking system is reportedly driving educated, middle-class Indians towards exploring other fintech avenues, especially for investment purposes. As per analytical reports shared by Indian crypto exchanges in December, 2022, Indians aged between 18-40 make for the maximum number of crypto investors.
Regulatory Landscape
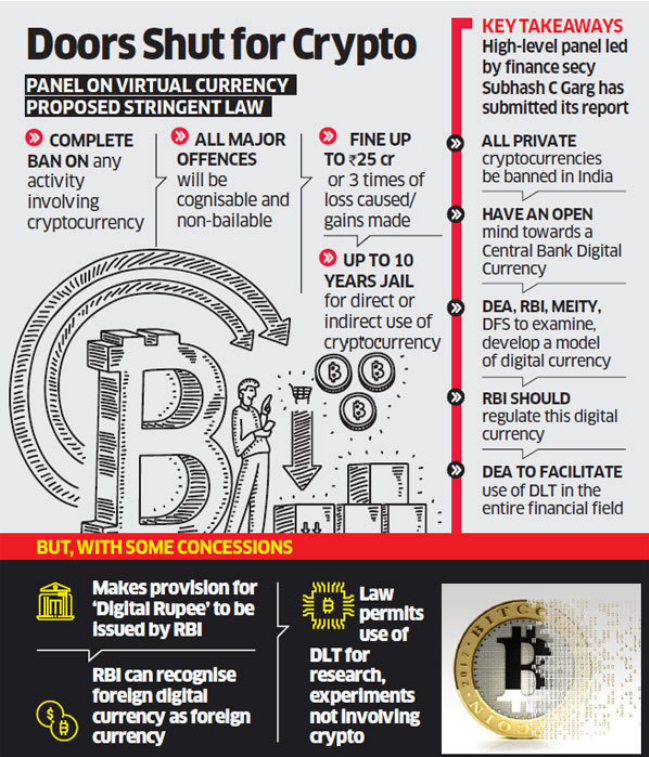
India
In India, cryptocurrency’s journey has been eventful. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) initially issued warnings against its use in 2017, leading to a brief ban on financial institutions dealing with cryptocurrencies. However, in March 2020, the Supreme Court of India overturned the ban, signaling a more favorable environment for cryptocurrencies
Recently, the Indian government introduced provisions to tax virtual digital assets (VDAs), including cryptocurrencies, as capital gains. The legal status of cryptocurrency in India remains unclear, as the government has yet to present the Cryptocurrency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2021, which will address the issue comprehensively.
Moreover, the RBI is considering the creation of India’s Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), known as the “Digital Rupee.” This move is expected to bolster India’s digital economy and enhance currency management.
Although cryptocurrency’s decentralized nature appeals to investors and traders, using it for settling payments or government dues may carry legal implications, as it isn’t recognized under the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999.
Global Regulatory Landscape
USA
Dual governance system, with states having different regulations. Positive approach overall, exemplified by New York’s BitLicense. Varied state regulations; generally, cryptocurrency is legal. federal agencies such as the CFTC (Commodity Futures Trading Commission), and FinCEN (Financial Crimes Enforcement Network).
United Kingdom
No specific legislation on cryptocurrency; not legal tender but considered property. Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) regulates authorized crypto-related businesses. Strict rules for businesses seeking FCA licensing. Crypto trading is taxed; follows corporate tax rules.
European Union
No specific legislation on cryptocurrency; not legal tender but considered property. Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) regulates authorized crypto-related businesses. Strict rules for businesses seeking FCA licensing. Crypto trading is taxed; follows corporate tax rules.
Canada
Cryptocurrency-friendly stance; viewed as an item for income tax purposes. Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) requires reporting of income or capital gain from crypto transactions. First country to accept a bitcoin-traded fund (ETF). Crypto exchanges are considered money service businesses, registered under FINTRAC.
While cryptocurrency continues to gain popularity around the globe, some countries shut their door for the alien infrastructure. Countries like Bangladesh, Egypt, China, Algeria, Turkey, Qatar and some others have banned the use and possession of cryptocurrency.
Conclusion

The crypto market in India has been growing at an exponential rate, driven by increased adoption facilitated by regulatory advancements, rising tech literacy, and a growing population seeking alternative investment opportunities. Revenue in the Cryptocurrencies market is projected to reach US$222.7m in 2023, and 328.70m users by 2027 and reflects the expanding user base and a diversified crypto ecosystem, with revenue streams from trading, decentralized finance, and innovative blockchain applications. User penetration will be 14.52% in 2023 and is expected to hit 22.37% by 2027, a combination of growing trust in cryptocurrencies, user-friendly platforms, and educational efforts is boosting adoption, widening the user base over time.
Crypto continues to gain popularity worldwide, on the other hand, it ends up being a nightmare. Crypto platform FTX collapses after it was revealed that the organization held assets as FTT and other token forms instead of fiat currency or any other market tested instruments.

